Over the last decade, the storage drive technology has evolved so much that upgrading your PC’s memory can get confusing. With the increasing options in the market and dozens of acronyms, it is hard to choose which one is the right one for you. Some popular comparisons are between the SSD vs. NVMe vs. M.2 Drives, the most popular version of storage drives.
So, which one is right for your PC to build?
Solid State Drives (SSDs) is the modern name used for reliable storage drives, which overtook the HDDs in size and speed. Now, the M.2 SATA and M.2 NVMe storage drives are the modern variants of SSDs, which are much smaller and faster. The typical M.2 drive refers to M.2 SATA, and NVMe refers to M.2 NVMe, which differs based on connection interfaces.
However, NVMe offers more efficient and faster access to non-volatile memory than M.2 or older SSDs. Notably, not all Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are the same, and each differs in speed, compatibility, and price. Therefore, we are going to compare the difference between SSD vs. NVMe vs. M.2 Drives in this article to see which is the right option for you.
What is an SSD Drive?

An SSD (Solid State Drive) is a computer storage device that offers significant advantages over traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). Unlike HDDs, which use spinning magnetic disks and mechanical read/write heads, SSDs use NAND-based flash memory to store data.
One of the most notable advantages of SSDs is their speed. Because they use flash memory, SSDs can access and transfer data much more quickly than HDDs. This leads to faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and improved system responsiveness.
Moreover, SSDs are more energy-efficient. They consume less power than traditional HDDs, and the SSD’s health can retain better than the HDDs. This energy efficiency, combined with their compact size and various form factors (such as 2.5-inch drives, M.2, and PCIe cards), allows SSDs to be easily integrated into various devices, from ultrabooks to high-performance desktop computers.
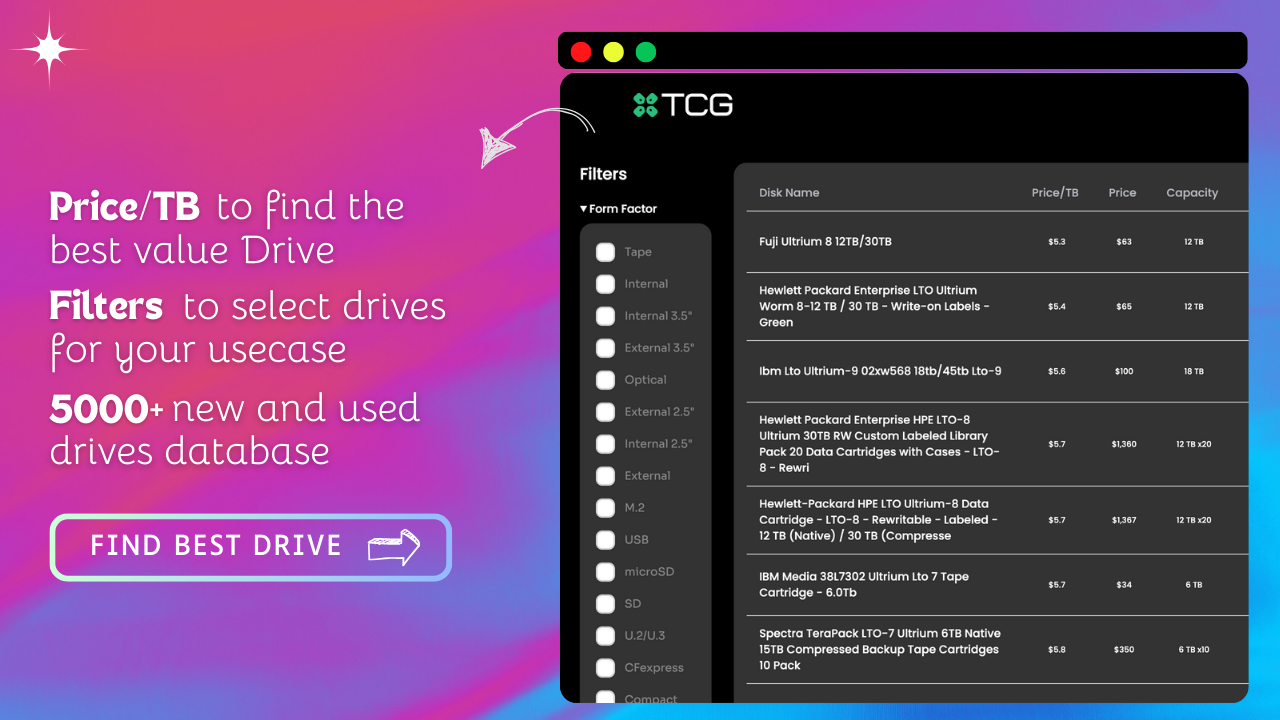
FInd the best SSD Drives for your budget, and get the most value for every dollar you spent on our disk price tool.
What is an M.2 Drive?
An M.2 drive is a type of solid-state drive (SSD) that uses the M.2 interface to connect to a computer’s motherboard. M.2 drives are known for their compact size and high performance, making them popular for modern laptops, desktops, and ultrabooks. The M.2 interface supports SATA (Serial ATA) and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) protocols, allowing for versatile and high-speed data transfer capabilities.
One of the key advantages of M.2 drives is their small form factor. They are typically much smaller than traditional 2.5-inch SSDs, allowing more efficient use of space inside a computer case. However, you won’t have to worry about low disk space as it has the same storage size as the typical SSD.
This compact size is particularly beneficial for ultrabooks and thin laptops, where space is premium. Despite their small size, M.2 drives can offer significant storage capacity, ranging from 128GB to multiple terabytes, depending on the model and manufacturer.
What is an NVMe Drive?

An NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) drive is an SSD designed to take full advantage of the high-speed PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) bus. Unlike traditional SATA SSDs, which are limited by the older SATA interface, NVMe drives utilize the PCIe interface to achieve much higher data transfer speeds.
The NVMe protocol was specifically developed to optimize the performance of SSDs. It reduces latency and increases input/output operations per second (IOPS) by streamlining the command set between the storage drive and the CPU.
Traditional storage protocols like AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) were designed with mechanical hard drives in mind and are not optimized for flash storage’s low-latency, high-speed capabilities. On the other hand, NVMe takes full advantage of the parallelism of modern CPUs and the inherent speed of flash storage, offering a significant boost in performance.
This combination of high speed, low latency, and flexibility in form factor and connection types makes NVMe drives a preferred choice for consumer and enterprise applications, offering enhanced performance and efficiency compared to traditional SSDs and HDDs.
Understanding the Difference Between PCIe and SATA
Before we jump into comparing which hard drive is better, it is important to understand the interfaces of hard drives to learn which one is more efficient.
What is SATA?

SATA is the older interface for PC motherboards that was launched back in 2003 and brought massive advancements to computer systems in its time. Originally, the SATA interface was designed for Hard Drives (HDDs), which was also adapted for SSDs.
What is PCIe?
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a newer interface that has a smaller physical footprint, making it more compact on the motherboard. PCIe’s major advantage over the SATA interface is the data transferring speed. The PCIe can transmit data on up to four lanes, while the SATA interface transfers data via only one. Therefore, the PCIe interface has better data transferring speeds than the SATA interface.
SSD vs. NVMe vs. M.2 Drives
| NVMe SSD | M.2 SATA SSD | SATA SSD | |
| Price Range (Depending on Storage) | $50 to $200 | $40 to $200 | $40 to $140 |
| Speed | PCIe 3rd Gen (up to 3500 MBPS) PCIe 4th Gen (up to 7500 MBPS) | Up to 550 MBPS | Up to 550 MBPS |
| For Factors | M.2, U.2, PCIe | (variable sizes) | 2.5-inch Drive |
| Interface Types | PCIe interface | SATA 6 Gb/s or USB 3.0 port | SATA |
| Advantages | Lightning-fast read-write speed | Consumes less space in your desktop PC | Perfect as an affordable but fast-speed drive |
| Disadvantages | Expensive | Can be more expensive than SATA SSD | Can add complexity to aesthetically oriented PC builds |
When comparing SSDs, NVMe drives, and M.2 drives, it’s important to understand that these terms often overlap but refer to different aspects of storage technology. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
SSD (Solid State Drive)
- Technology: SSDs use NAND flash memory to store data. They have no moving parts, making them faster and more reliable than traditional HDDs.
- Performance: SSDs are significantly faster than HDDs, with quicker boot times, faster file transfers, and better overall system responsiveness.
- Interfaces: SSDs typically connect via SATA (Serial ATA) or PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interfaces. SATA SSDs are limited by the SATA interface speed, usually up to 600 MB/s.
- Form Factors: Common form factors include 2.5-inch (similar to laptop HDDs) and M.2 (a small, stick-like form factor).
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express)
- Technology: NVMe is a protocol designed specifically for SSDs to maximize the performance potential of flash memory by utilizing the high-speed PCIe interface.
- Performance: NVMe drives offer significantly higher data transfer speeds compared to SATA SSDs. They can reach speeds up to 3500 MB/s or higher, depending on the number of PCIe lanes they use.
- Latency and IOPS: NVMe drives have lower latency and higher Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS), making them ideal for high-performance tasks like gaming, video editing, and large-scale data processing.
M.2 Drives
- Form Factor: M.2 is a form factor for SSDs that looks like a stick of gum. M.2 drives can be either SATA-based or NVMe-based.
- Interfaces: M.2 drives can connect via either SATA or PCIe interfaces. NVMe M.2 drives use the PCIe interface, while SATA M.2 drives use the SATA interface.
- Performance: The performance of an M.2 drive depends on whether it is SATA-based or NVMe-based. SATA M.2 drives offer similar performance to 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, while NVMe M.2 drives leverage the PCIe interface to achieve much higher speeds.

NVMe, M.2, and SSD: Which One is Better?
If you are not sure which SSD to install on your PC, then here are some use cases that might help you to make the right choice.
- SATA SSDs: Suitable for general computing, upgrading older systems, and cost-effective storage solutions.
- NVMe SSDs: Ideal for high-performance tasks such as gaming, video editing, and data-intensive applications.
- M.2 SATA: Good for compact systems where space is limited but high performance is not critical.
- M.2 NVMe: Best for high-performance needs in compact systems.

FAQs
Is NVMe Better for Gaming than M.2 Drive?
Yes, NVMe has a much faster data transferring speed as compared to M.2 Drives or SSD SATA drives, which is why it is a much better option.
Are NVMe and M.2 Drives the Same?
No, the M.2 is a compact form factor of SSD SATA, while the NVMe is the interface that connects with the motherboard. The main difference is the interface; hence, the M.2 NVMe and M.2 SATA differ.
Is the M.2 Faster than the SSD?
Even though M.2 is the smaller version of SSD SATA and it has pretty much the same storage space, the M.2 drive is a bit faster than the SSD in some cases.
Conclusion
While all SSDs offer improved performance over traditional HDDs, NVMe drives stand out for their superior speed and low latency, making them the best choice for high-performance tasks like gaming. M.2 drives provide flexibility in form factor, with the added benefit of NVMe speeds when using the PCIe interface. Hence, it is totally up to your PC’s compatibility or budget to choose the right storage drive. Hopefully, this article has guided you well on the difference between SSD vs. NVMe vs. M.2 Drives.